The automotive world is buzzing with anticipation. Toyota, a giant known for its hybrid prowess and cautious approach to full electrification, has announced plans to introduce solid-state batteries in its electric vehicles by 2027. This isn't just another EV announcement; it's a potential game-changer. But can they really pull it off?
For years, drivers looking toward an electric future have faced similar concerns: range anxiety, long charging times, and the overall cost of EVs. These concerns are valid and often prevent potential buyers from making the switch. While battery technology has improved, a truly disruptive advancement is needed to overcome these hurdles.
This article delves into Toyota's ambitious plan to launch EVs with solid-state batteries by 2027. We'll explore the potential benefits of this technology, examine the challenges Toyota faces, and consider the likelihood of their success in revolutionizing the EV landscape.
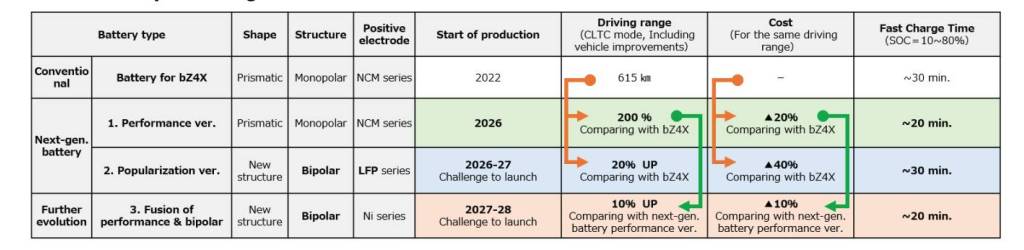
Toyota's commitment to solid-state batteries marks a significant shift in the EV race. These batteries promise faster charging times, greater energy density (leading to longer range), and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, mass production of solid-state batteries is notoriously difficult and expensive. Toyota's success hinges on overcoming these manufacturing hurdles and proving the durability and reliability of this next-generation battery technology. Key terms include solid-state batteries, electric vehicles, EV battery technology, Toyota, range anxiety, charging times, and energy density.
The Promise of Solid-State Batteries
The whole concept of solid-state batteries has me reminiscing about a science fair project I did back in high school. I attempted to build a rudimentary fuel cell, fueled mostly by optimism and You Tube tutorials. It was a spectacular failure, but it gave me a deep appreciation for the complexities of energy storage. Seeing Toyota, a company with a reputation for engineering excellence, tackle this challenge feels like watching a real-world, high-stakes version of my old science project. The potential impact on the automotive industry and the environment is massive.
Solid-state batteries are poised to revolutionize the EV market by offering significant improvements over traditional lithium-ion batteries. One of the key advantages is their higher energy density. This means that a solid-state battery pack can store more energy for the same size and weight compared to a lithium-ion pack, resulting in longer driving ranges for EVs. Imagine being able to drive hundreds of miles on a single charge without having to worry about finding a charging station. This would alleviate range anxiety, a major concern for many potential EV buyers. Furthermore, solid-state batteries are expected to charge much faster than lithium-ion batteries, potentially reducing charging times to just a few minutes. This would make EV ownership much more convenient and appealing to a wider range of consumers. Finally, solid-state batteries are inherently safer than lithium-ion batteries because they use a solid electrolyte instead of a flammable liquid electrolyte, reducing the risk of fires and explosions. The combination of these benefits makes solid-state batteries a very promising technology for the future of EVs.
Toyota's Strategy: A Calculated Risk?
Toyota's approach to electric vehicles has been often described as cautious. While other manufacturers dove headfirst into battery electric vehicles (BEVs), Toyota focused on perfecting hybrid technology and exploring alternative fuel sources like hydrogen. This strategy, while criticized by some, allowed Toyota to build a strong foundation in electrification and develop a deep understanding of battery technology. Now, with solid-state batteries on the horizon, Toyota is making a bold move that could redefine its position in the EV market. The question is whether their calculated approach will pay off in the long run, or if they've waited too long to embrace full electrification.
Toyota's strategy is a calculated risk because while they've been perfecting hybrid technology, other companies have been focused on battery electric vehicles. The risk that Toyota is taking is that they might lose market share to these other companies while they perfect solid-state batteries. But the potential reward is that they could leapfrog the competition by introducing a superior battery technology that offers longer range, faster charging times, and improved safety. The EV landscape is constantly evolving, and there's no guarantee that Toyota's bet will pay off, but it's certainly a strategy that could make them a major player in the future of electric vehicles.
The History and the Hype: Solid-State Batteries Through the Ages
The idea of solid-state batteries isn't exactly new. Scientists have been experimenting with them for decades, but the technology has always faced significant hurdles in terms of scalability and cost-effectiveness. The "hype" surrounding solid-state batteries has ebbed and flowed over the years, with promising breakthroughs often followed by setbacks. The current wave of excitement is fueled by advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques, as well as the growing demand for better EV batteries. Toyota's announcement has certainly added fuel to the fire, but it's important to remember that the path to commercializing solid-state batteries is still fraught with challenges.
While the concept of solid-state batteries has been around for quite some time, the actual development and refinement of the technology have been a long and arduous process. Early research faced challenges related to finding suitable solid electrolytes with high ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability. Materials that showed promise in the lab often failed to perform adequately in real-world conditions. Manufacturing these batteries at scale has also been a significant obstacle, as the processes required for solid-state battery production are often more complex and expensive than those used for traditional lithium-ion batteries. Despite these challenges, scientists and engineers have continued to make progress, and the recent advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have brought solid-state batteries closer to commercialization than ever before. Toyota's announcement is just one example of the growing optimism surrounding this technology, but it's important to approach the hype with a healthy dose of realism. The road to mass production of solid-state batteries is still a long one, and there are many potential pitfalls along the way.
Unveiling the Secrets: What Makes Solid-State Batteries Different?
The "secret" to solid-state batteries lies in the replacement of the liquid electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte. This seemingly simple change has profound implications for battery performance, safety, and lifespan. Solid electrolytes can be made from various materials, including ceramics, polymers, and sulfides. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and cost. The choice of electrolyte material is crucial for achieving the desired battery performance characteristics.
The use of a solid electrolyte in solid-state batteries offers several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries with liquid electrolytes. One of the key benefits is improved safety. Liquid electrolytes are often flammable and can pose a fire hazard in the event of a battery malfunction. Solid electrolytes, on the other hand, are non-flammable and inherently safer. Another advantage is increased energy density. Solid electrolytes enable the use of high-voltage and high-capacity electrode materials that are not compatible with liquid electrolytes, allowing for greater energy storage in a smaller volume. Solid-state batteries also have the potential for longer lifespans and improved performance at extreme temperatures compared to lithium-ion batteries. The shift from liquid to solid electrolyte is a fundamental change that unlocks a range of possibilities for battery technology.
Recommendation of Toyota Plans Solid-State EV Battery by 2027
If you're currently in the market for an EV, it might be tempting to hold off until 2027 to see if Toyota's solid-state batteries live up to the hype. However, technology moves quickly, and there are plenty of excellent EVs available today that offer impressive range, performance, and features. My recommendation is to research your options carefully, consider your driving needs, and choose an EV that meets your requirements. Don't let the promise of future technology paralyze you from making a decision that could benefit you today.
Of course, keeping an eye on the development of solid-state battery technology is a good idea, especially if you're planning to purchase an EV in the next few years. Monitor industry news and expert opinions to stay informed about the progress of this technology and its potential impact on the EV market. When Toyota's solid-state batteries become commercially available, it will be a good time to re-evaluate your EV options and see if they offer a significant advantage over existing battery technologies. In the meantime, there are many excellent EVs available that can meet your needs. Consider factors such as range, charging time, performance, and price when making your decision.
The Challenges Ahead: Can Toyota Overcome the Hurdles?
While the potential benefits of solid-state batteries are clear, significant challenges remain in bringing this technology to mass production. One of the biggest hurdles is manufacturing. Producing solid-state batteries at the scale required for the automotive industry is a complex and expensive process. Toyota will need to invest heavily in new manufacturing facilities and develop efficient production techniques to meet its 2027 target. Another challenge is durability. Solid-state batteries need to withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation in performance. Toyota will need to conduct rigorous testing to ensure that its solid-state batteries are reliable and long-lasting.
Another critical hurdle that Toyota needs to clear is the cost of materials. Some of the materials used in solid-state batteries, such as certain ceramic electrolytes, can be quite expensive. Toyota will need to find ways to reduce the cost of these materials or develop alternative materials that are more affordable. Scalability is another significant challenge. Even if Toyota can successfully produce solid-state batteries on a small scale, scaling up production to meet the demands of the automotive industry will require significant investments in infrastructure and expertise. Furthermore, the performance of solid-state batteries can be affected by factors such as temperature and humidity. Toyota will need to develop strategies for mitigating these effects to ensure that its solid-state batteries perform reliably in a wide range of environments. Overcoming these challenges will require significant innovation and collaboration across various disciplines, including materials science, engineering, and manufacturing. Toyota's success in bringing solid-state batteries to mass production will depend on its ability to effectively address these technical and economic hurdles.
Toyota's Technological Prowess: Is It Enough?
Toyota has a well-deserved reputation for engineering excellence and technological innovation. The company has a long history of developing and deploying advanced technologies in its vehicles, including hybrid powertrains, advanced safety systems, and autonomous driving features. This technological prowess gives Toyota a significant advantage in the race to commercialize solid-state batteries. However, success is not guaranteed. Toyota will need to leverage its expertise in materials science, manufacturing, and battery management to overcome the challenges of mass production and ensure the reliability and durability of its solid-state batteries.
Toyota's expertise in materials science is particularly relevant to the development of solid-state batteries. The company has been investing in research and development of advanced materials for many years, and it has a deep understanding of the properties and performance of various materials. This knowledge will be crucial for selecting the right materials for the solid electrolyte and electrodes in its solid-state batteries. Toyota's manufacturing capabilities are also a key advantage. The company has a proven track record of mass-producing high-quality vehicles and components, and it has the infrastructure and expertise to scale up production of solid-state batteries to meet the demands of the automotive industry. Furthermore, Toyota's battery management systems are among the most advanced in the industry. These systems are designed to optimize battery performance, extend battery life, and ensure battery safety. This expertise will be essential for ensuring that Toyota's solid-state batteries perform reliably and safely in its electric vehicles. While Toyota's technological prowess is a significant advantage, the company will still need to overcome significant technical and economic hurdles to bring solid-state batteries to mass production.
Expert Opinions: What Are the Industry Analysts Saying?
Industry analysts are generally optimistic about the potential of solid-state batteries, but they also acknowledge the significant challenges that remain. Some analysts believe that Toyota has a good chance of succeeding in its 2027 target, given the company's technological expertise and financial resources. Others are more cautious, pointing to the difficulties of mass production and the potential for unexpected technical setbacks. The consensus seems to be that solid-state batteries are the future of EV batteries, but the timeline for their widespread adoption is still uncertain.
One of the main concerns among industry analysts is the cost of solid-state batteries. Currently, the materials and manufacturing processes required for solid-state batteries are more expensive than those used for traditional lithium-ion batteries. Toyota will need to find ways to reduce the cost of solid-state batteries to make them competitive with lithium-ion batteries. Another concern is the durability of solid-state batteries. While solid-state batteries are generally considered to be more durable than lithium-ion batteries, they still need to withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation in performance. Toyota will need to conduct rigorous testing to ensure that its solid-state batteries are reliable and long-lasting. Furthermore, industry analysts are closely watching the progress of other companies in the solid-state battery space. Several other automakers and battery manufacturers are also working on solid-state batteries, and it's possible that one of these companies could beat Toyota to market. The competition in the solid-state battery space is intense, and the race to commercialize this technology is far from over.
Fun Facts: Solid-State Battery Edition
Did you know that the first solid-state battery was actually developed in the 1950s? However, it was too expensive and inefficient to be practical for widespread use. Fast forward to today, and advancements in materials science have made solid-state batteries a much more viable option. Another fun fact: some solid-state batteries can operate at much higher temperatures than traditional lithium-ion batteries, making them suitable for use in extreme environments. The world of battery technology is full of fascinating facts and innovations!
Solid-state batteries aren't just about better performance; they also open up possibilities for entirely new battery designs. Because they don't rely on a liquid electrolyte, they can be made smaller and lighter, which is crucial for applications like wearable devices and drones. Imagine a smartwatch that lasts for weeks on a single charge, or a drone that can fly for hours without needing a battery swap. Solid-state batteries could make these scenarios a reality. And speaking of drones, solid-state batteries are also being explored for use in electric aircraft. The higher energy density and improved safety of solid-state batteries could enable longer flight times and reduce the risk of battery fires in these applications. The potential applications of solid-state batteries are vast and span across a wide range of industries.
How to: Follow Toyota's Solid-State Battery Progress
Staying informed about Toyota's solid-state battery development is relatively straightforward. Follow reputable automotive news outlets, subscribe to industry newsletters, and keep an eye on Toyota's official press releases. Also, look for expert analysis from battery technology experts and industry analysts. Be wary of overly sensationalized headlines and focus on factual reporting and data-driven analysis. The goal is to stay informed without getting caught up in the hype.
Social media can also be a useful source of information, but it's important to be discerning. Follow credible sources, such as established automotive news organizations and battery technology experts. Be wary of anonymous accounts and unsubstantiated claims. Participate in online forums and discussions, but always verify the information you read before accepting it as fact. Another way to stay informed is to attend industry conferences and events. These events provide opportunities to hear presentations from experts, network with industry professionals, and see the latest battery technology developments firsthand. Finally, consider subscribing to research reports from market research firms that specialize in battery technology. These reports can provide in-depth analysis of the market trends, technological advancements, and competitive landscape in the solid-state battery space.
What If: Toyota Fails to Deliver on its 2027 Promise?
What if Toyota doesn't meet its 2027 deadline for launching EVs with solid-state batteries? While it would be a setback for Toyota, it wouldn't necessarily mean the end of the road for solid-state battery technology. Other companies are also working on solid-state batteries, and they may be able to bring their products to market sooner. Even if solid-state batteries take longer to commercialize than expected, battery technology will continue to evolve, with advancements in lithium-ion batteries and other battery chemistries.
If Toyota fails to deliver on its 2027 promise, it could have several consequences for the company. First, it could damage Toyota's reputation as a technological leader. The company has built a strong brand image based on its reputation for quality and innovation, and failing to deliver on a major technological promise could erode that image. Second, it could give Toyota's competitors a competitive advantage. If other automakers are able to bring solid-state batteries to market before Toyota, they could gain a significant edge in the EV market. Third, it could delay Toyota's transition to electric vehicles. The company has been slower to embrace EVs than some of its competitors, and a delay in the development of solid-state batteries could further slow down its transition. However, even if Toyota fails to meet its 2027 deadline, it's important to remember that the company has a long history of innovation and resilience. Toyota has overcome many challenges in the past, and it's likely that it would be able to adapt and recover from this setback.
Listicle: 5 Reasons Why Toyota's Solid-State Battery Plan Matters
Here are 5 reasons why Toyota's solid-state battery plan is significant:
- It could revolutionize EV range, addressing range anxiety concerns.
- Faster charging times could make EV ownership more convenient.
- Improved safety features enhance the appeal of EVs.
- It signals a major shift in Toyota's EV strategy.
- It could accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles worldwide.
But let's dig a little deeper into each of these points. Longer range isn't just about bragging rights; it's about practicality. It's about being able to take a road trip without constantly worrying about finding charging stations. It's about being able to use your EV for all your daily needs without having to plug it in every night. Faster charging times are equally important. No one wants to spend hours waiting for their car to charge. Solid-state batteries could significantly reduce charging times, making EV ownership much more convenient. Improved safety is always a plus. Solid-state batteries are inherently safer than lithium-ion batteries, reducing the risk of fires and explosions. Toyota's plan also signals a major shift in the company's EV strategy. Toyota has been slow to embrace EVs, but its commitment to solid-state batteries suggests that the company is finally serious about electrification. Finally, Toyota's plan could accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles worldwide. If Toyota is successful in bringing solid-state batteries to market, it could help to make EVs more affordable, practical, and appealing to a wider range of consumers. The impact of solid-state batteries could truly transform the EV industry.
Question and Answer: Toyota's Solid-State Battery Ambitions
Here are some common questions and answers about Toyota's plans:
Q: What are solid-state batteries?
A: Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, offering potential advantages in energy density, safety, and charging speed.
Q: Why is Toyota focusing on solid-state batteries?
A: Toyota believes solid-state batteries represent a breakthrough technology that can overcome the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries.
Q: What are the challenges of producing solid-state batteries?
A: Mass production is difficult and expensive, and ensuring durability and reliability is crucial.
Q: What happens if Toyota doesn't meet its 2027 target?
A: It could face competitive disadvantages, but other companies are also developing solid-state batteries, and battery technology continues to evolve.
Conclusion of Toyota Plans Solid-State EV Battery by 2027
Toyota's plan to introduce solid-state batteries by 2027 is a bold move that could reshape the electric vehicle landscape. While significant challenges remain, the potential benefits of this technology are undeniable. Whether Toyota can successfully execute its plan remains to be seen, but one thing is certain: the race to develop and commercialize solid-state batteries is heating up, and the future of electric vehicles is looking brighter than ever.